This repo documents Docker images for geographic research and reproducing code in the books Geocomputation with R and Geocomputation with Python. The Dockerfiles build on work done for the Rocker Project. As documented on the Rocker Project website, Docker can save time and increase reproducibility by providing an environment with up-to-date and stable software.
To get started, after you install Docker, try running one of the following commands:
# The latest version of rocker/geospatial + geocompr dependencies
docker run -e PASSWORD=pw --rm -p 8786:8787 ghcr.io/geocompx/docker
# With up-to-date OSGeo packages and qgisprocess:
docker run -e PASSWORD=pw --rm -p 8786:8787 ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:osgeoIf you are asked for a username and password, then you should use
rstudio as your username and the password you set with the above code
(e.g., pw).
Then open a browser at http://localhost:8786/, and you should see something like this:
If so congratulations 🎉 you can proceed to open the geocompr.Rproj
project or other files in the geocompr folder, which contains a
complete copy of the source code and example data needed to build the
html version of the book.
To run a container without RStudio, try the following.
docker run -e PASSWORD=pw --rm -ti ghcr.io/geocompx/docker /bin/bash
Use this resource to play with the examples, develop new answers to the questions at the end of each page, or even to generate reproducible examples to illustrate issues with the books contents.
If not, see documentation on using Docker at websites such as docker.com and https://www.rocker-project.org/.
To use these Docker images for your own work you will need to share
files with Docker. That means sharing ‘volumes’. You can do this using
the -v argument as shown below, which shares your current working
directory with the Docker container. If you run these commands in a
terminal that has access to Docker, like bash or Windows PowerShell
you should get a local copy of Geocomputation with R on your computer
that you can use for testing and development purposes, e.g. to test
changes before submitting a Pull Request to improve the book:
# download repo with Windows Powershell or a Unix terminal
git clone https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr.git
# or download manually from https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/archive/main.zip
cd geocompr # navigate into the repo
# on linux and mac with password:
docker run -d -p 8786:8787 -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/data -e USERID=$UID -e PASSWORD=pw ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:minimal
# on linux and mac without password:
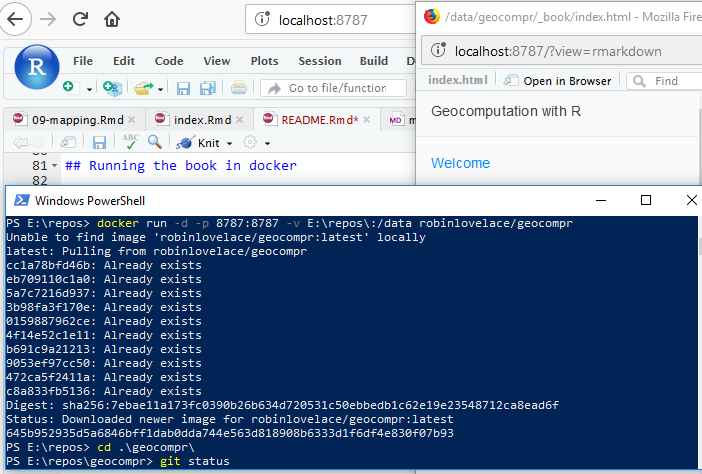
docker run -d -p 8786:8787 -e DISABLE_AUTH=TRUE -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/geocompr ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:minimalIf you see something like this after following the steps above, congratulations: it worked! See github.com/rocker-org for more info.
You can also pull and run the same images from ghcr.io, e.g. as follow:
docker run -d -p 8786:8787 -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/data -e PASSWORD=pw ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:minimalFrom this point to build the book you can open projects in the
geocompr directory from the project box in the top-right hand corner,
and knit index.Rmd with the little knit button above the the RStudio
script panel (Ctl+Shift+B should do the same job).
There are various versions of the geocompr Docker image available. The
default is the latest tag, representing the Dockerfile in the root
of this repo, but you can get other images, as outlined below.
Building on the rocker-org project, we provide various versions for testing and development, including builds that use more up-to-date versions of OSGeo packages such as GDAL provided by the UbuntuGIS software repository, as shown below:
| image | description | size |
|---|---|---|
| docker:latest | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:latest image + book files | |
| docker:minimal | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:minimal rocker/geospatial plus geocompkg Imports | |
| docker:suggests | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:suggests includes all packages from geocompkgs (Suggests) | |
| docker:binder | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:binder runs with Binder | |
| docker:osgeo | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:osgeo running on rocker/geospatial:osgeo | |
| docker:buildbook | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:buildbook runs the book code | |
| docker:qgis | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:qgis with QGIS | |
| docker:rocker-rpy | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:rocker-rpy with python | |
| docker:rocker-rpyjl | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:rocker-rpyjl with R, Python, and Julia | |
| docker:python | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:python Python image + geo pkgs | |
| docker:rust | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:rust with Rust | |
| docker:pixi-r | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:pixi-r | |
| docker:pixi-py | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:pixi-py | |
| docker:pixi-rpy | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:pixi-rpy | |
| docker:mamba-py | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:mamba-py | |
| docker:mamba-pyr | docker pull ghcr.io/ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:mamba-pyr |
The base image is rocker/geospatial from
github.com/rocker-org/rocker-versioned2.
Add :tagname after ghcr.io/geocompx/docker to get the image you want.
docker run -e PASSWORD=pw --rm -p 8786:8787 ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:buildbookFor reasons we don’t understand on the pixi side, you must set the locale with something like
"postCreateCommand": "apt update && apt install -y --no-install-recommends locales; echo \"en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8\" >> /etc/locale.gen; locale-gen",
If you use these in a devcontainer.
To test your code or package against recent versions of OSGeo libraries (GDAL, GEOS, PROJ), you can run the following command from inside root directory of the folder containing the code:
# on linux and mac with password:
docker run -d -p 8786:8787 -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/data \
-e USERID=$UID -e PASSWORD=pw ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:osgeoThe Python tag contains Python geospatial packages:
docker run -e PASSWORD=pw --rm -ti ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:python /bin/bash
python3
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
import movingpandas as mpdYou can run an interactive session via Reticulate in RStudio as follows:
docker run -e PASSWORD=pw --rm -p 8786:8787 ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:pythonAnd then in the resulting RStudio session you can enter something along the lines of:
library(sf)
f = file.path(system.file("shape/nc.shp", package="sf"))
nc_sf = read_sf(f)
library(reticulate)
system("pip3 install descartes")
gp = import("geopandas")
nc_gp = gp$read_file(f)
class(nc_gp)
plot(nc_gp$AREA, nc_gp$PERIMETER)
gp = import("geopandas", convert = FALSE)
nc_gp = gp$read_file(f)
nc_gp
plt = import("matplotlib.pyplot", convert = FALSE)
nc_gp$plot()
plt$savefig("test.png")To plot from Python packages (work in progress).
To run QGIS from the command line, you can run:
docker pull ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:qgis
docker run --rm -ti ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:qgis /bin/bash
qgis --version
# QGIS 3.20.3-Odense 'Odense' (495fbaecaf)You can also run QGIS algorithms via the qgisprocess package as
follows:
docker run -d -p 8786:8787 -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/data -e PASSWORD=pw ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:qgis
Then open a browser and the local url such as http://192.168.0.99:8786/ or http://localhost:8786, enter RStudio server, and you should be able to access QGIS as follows in the R console:
system("qgis --version")
## QGIS 3.16.1-Hannover 'Hannover' (b381a90dca)
remotes::install_github("paleolimbot/qgisprocess") # install the latest version of the package
qgis_algs = qgisprocess::qgis_algorithms()
nrow(qgis_algs)
## [1] 303
table(qgis_algs$provider)
## 3d gdal native qgis
## 1 55 196 51 You can access algorithms from other GIS programs through QGIS but they
need to be installed. These can be accessed from the
ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:qgis image as follows:
docker run -d -p 8786:8787 -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/data -e PASSWORD=pw ghcr.io/geocompx/docker:qgis
Again, open the browser, e.g. at http://localhost:8786, and find the new algorithms as follows:
system("qgis --version")
## QGIS 3.16.1-Hannover 'Hannover' (b381a90dca)
remotes::install_github("paleolimbot/qgisprocess") # install the latest version of the package
## Skipping install of 'qgisprocess' from a github remote, the SHA1 (6e378511) has not changed since last install.
qgis_algs = qgisprocess::qgis_algorithms()
nrow(qgis_algs)
## [1] 970
table(qgis_algs$provider)
## 3d gdal grass7 native qgis saga
## 1 55 301 196 51 366 Congratulations, you now have nearly 1000 QGIS algorithms at your disposal from the R command line 🎉
You can build the images locally, e.g. as follows:
docker build qgis -t test
docker run -p 8888:8888 test
docker build conda -t geocompy
docker run -it geocompy /bin/bash
docker build -t You should then be able to run commands in the newly created images, e.g. with:
docker run -it /bin/bash